Using cross-origin resource sharing
1. Overview
This article explains how to enable and use Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS). This allows your web application's JavaScript to communicate with the Dundas or Logi Symphony APIs or embedded application, even if these are hosted on two different domains.
2. Configuration
Cross-origin resource sharing must be configured to enable either of these two types of communication with Dundas BI or Logi Symphony's Managed Dashboards & Reports from your own client-side application's JavaScript:
- Communication with the server via its API, including iframeless embedding, if the URLs for your application and Dundas BI or Logi Symphony have different domains or origins.
- Communication with the client application embedded on your page in an iframe or using the embed library, even if both applications have the same domain/origin.
While logged on as a member of the System Administrators group, access the administration area from the main menu on the left.
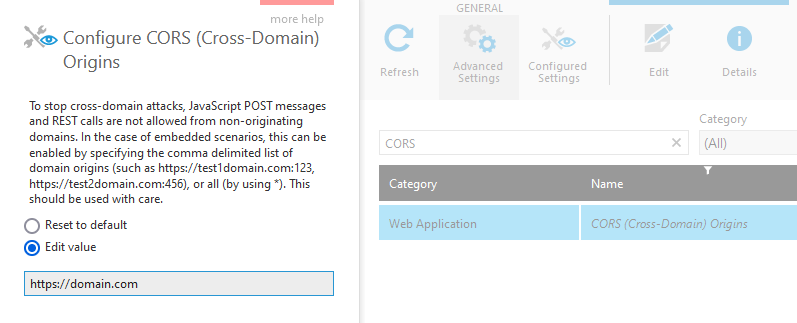
Click to expand Setup and select Config to edit configuration settings. Find and click to edit the setting CORS (Cross-Domain) Origins in the Web Application category, ensuring the option to show Advanced Settings is selected.
Edit this setting to enter the URL origin(s). This lets the application know that the origin/domain you specify is yours and is authorized to make API calls from the browser or to communicate with the embedded iframe.
Any site with a different origin not listed or included is prevented by browsers from accessing the APIs, and cannot pass an embedded application any messages. No script from posted messages will be executed as in examples below unless the embedding application's origin is listed or included even if the same as Dundas BI or Logi Symphony.
Click to Save your changes at the bottom of the dialog.
3. Cross-origin script example
The following is an example of cross-origin resource sharing, where your own application's JavaScript passes JavaScript to run in the client application embedded within yours in the browser.
For the examples in this article where the application is embedded on the page, it is embedded using an inline frame (iframe). You can also use the embed library and use its runScript method. See also the viewer integration sample.
3.1. Create a new dashboard
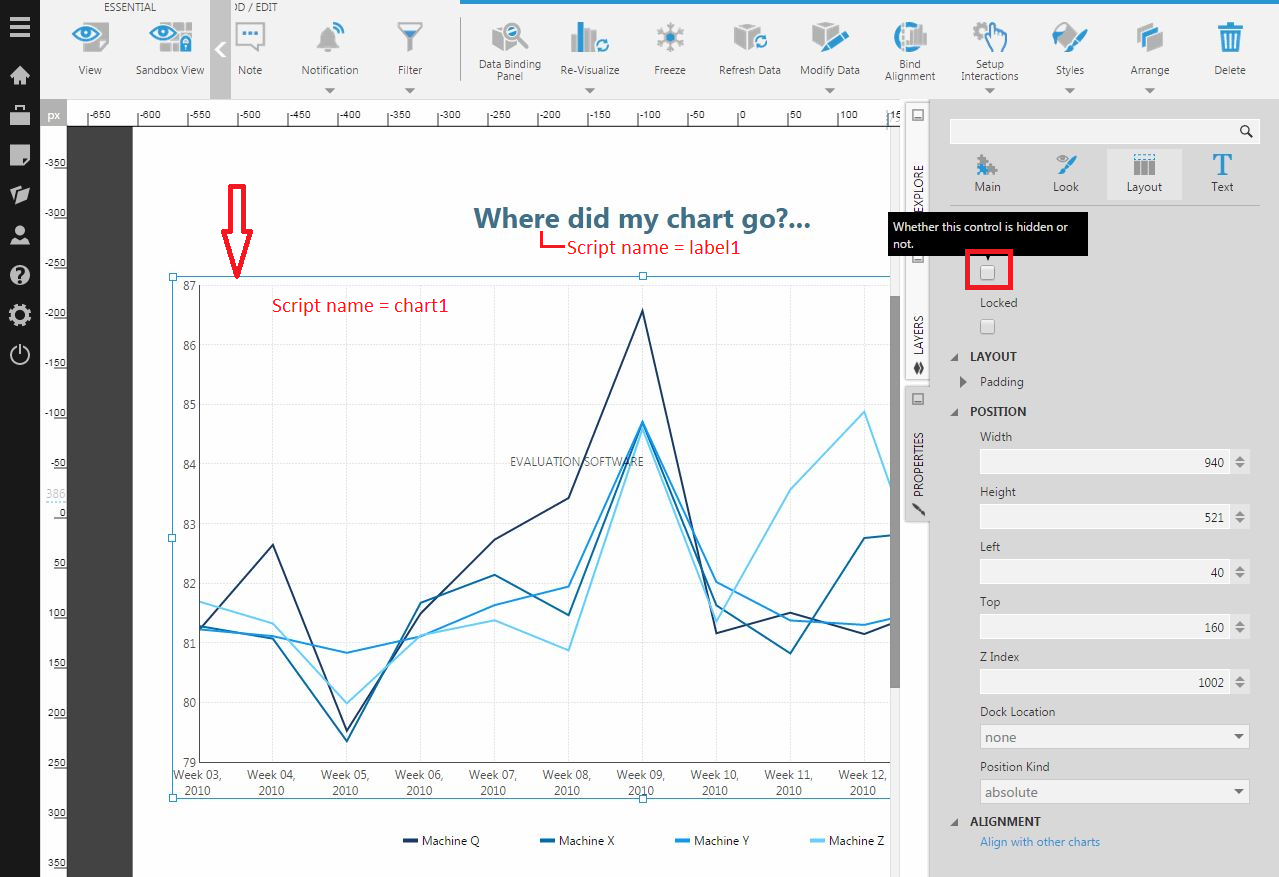
On a new dashboard, add a chart (with Script Name chart1) and a label (with the Script Name label1).
For this example, we will be altering the text in the label and unhiding the chart. This will be done by sending a script from the host site into the iframe embedding the application.
Select the Hidden property of the chart, which is located in the Properties window in the Layout tab.
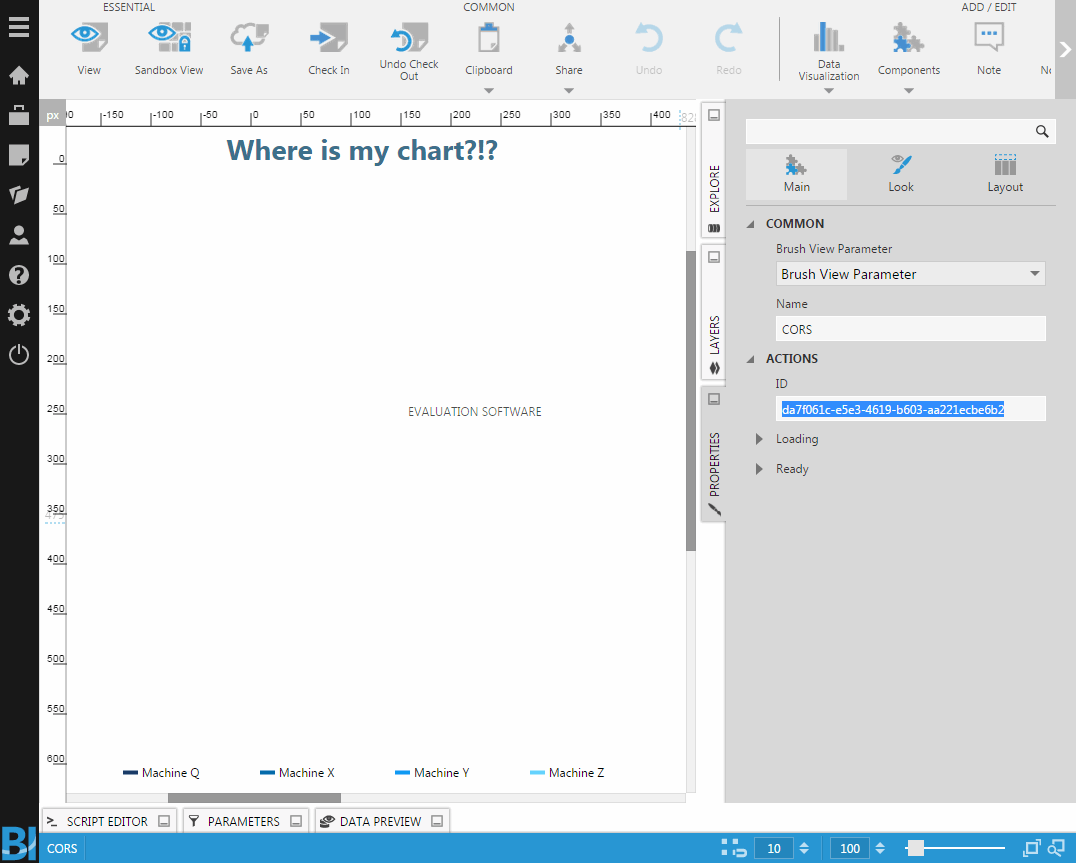
In the Dashboard's properties, copy the dashboard ID from the Main tab.
Now check in the dashboard, and embed this file by its ID into your web application.
3.2. Add the CORS JavaScript
JavaScript like the following could be added to your application/page, which calls postMessage. This particular example assumes a jQuery library reference is included on the page:
$(document).ready(function () {
// Synchronous Example
var element = $("iframe").get(0);
$(element).load(function () {
// Since the iframe will have loaded before the dashboard has,
// we need to pass in a function that runs when the dashboard is ready.
element.contentWindow.postMessage({
"isAsync": false,
"script": "\n\
window.dundas.context.ready(function () {\n\
var myView = dundas.context.baseViewService.currentView;\n\
var myLabel = myView.getAdapters().filter(function(a) { return a.name == \"label1\" })[0];\n\
var myChart = myView.getAdapters().filter(function(a) { return a.name == \"chart1\" })[0];\n\
myChart.hidden = false;\n\
myLabel.labelText = \"There it is!!!\";\n\
});\n\
"
}, "https://dundas.example.com");
});
});
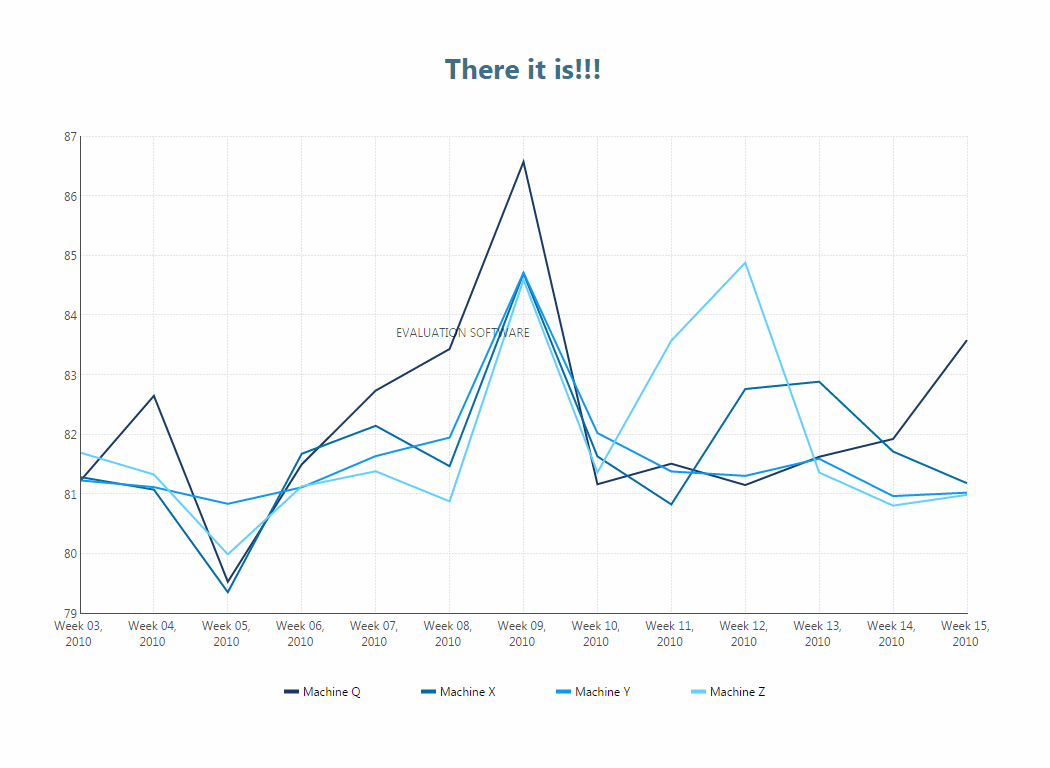
The script sent to the embedded client application waits for the dashboard to load, then finds and modifies the properties of the chart and label.
The \n\ is required to include the line breaks in the string.
3.3. Test sample
Build and publish your project's server-side changes (if applicable).
You should now see the new label text and the chart should be visible.
4. Other CORS JavaScript examples
4.1. Change view options and return data
The following is another example of running JavaScript within the embedded client application from your own application's JavaScript. It sets the view options of a dashboard to hide the menu, toolbar and taskbar, then sends a message back to the parent application.
$(document).ready(function() {
// Hook up to receive window postMessage calls.
$(window).bind("message", function (e) {
var result = e.originalEvent.data;
// result will be ‘hi’
});
// Synchronous Example
var iframe = $("#iFrame").get(0);
$(iframe).load(function() {
iframe.contentWindow.postMessage({
"isAsync": false,
"script": " console.log(e);
window.dundas.context.baseViewService.viewOptions = dundas.ViewOptions.VIEW_ONLY;
window.dundas.context.updateViewFromViewOptions();
return 'hi';
"
}, "https://dundas.example.com");
});
});
4.2. Change view options and return data asynchronously
The following example is the same as the previous but sends a message back to the parent application asynchronously (when a timeout expires, for demonstration purposes). The isAsync property is set to true in the posted message object, in which case the accompanying script should return a jQuery Promise or Deferred as done below:
$(document).ready(function() {
// Hook up to receive window postMessage calls.
$(window).bind("message", function (e) {
var result = e.originalEvent.data;
// result will be ‘hi’
});
// Asynchronous Example
var iframe = $("#iFrame").get(0);
$(iframe).load(function() {
iframe.contentWindow.postMessage({
"isAsync": true,
"script": " console.log(e);
window.dundas.context.baseViewService.viewOptions = dundas.ViewOptions.VIEW_ONLY;
window.dundas.context.updateViewFromViewOptions();
var result = new $.Deferred();
window.setTimeout(function() {
result.resolve('hi')
}, 500);
return result.promise();
"
}, "https://dundas.example.com");
});
// Note that ‘e’ is the original message's event, so you can also use e.source.postMessage(..)
// to send a message back in addition to returning a value.
});
5. REST API example
The following example sends a /Dashboard/ request to the server from your own application's JavaScript. In this case, there may not be any embedded application on the page.
$(document).ready(function() {
// REST API example
var def = $.ajax("https://dundas.example.com/api/dashboard/[dashboardId]",
{ headers: { "Authorization": "Bearer " + sessionId } }
);
def.done(function (dashboard) {
// perform action here.
});
// Note that this method returns a plain object rather than a full Dundas class instance
});
6. Troubleshooting
Use your browser's developer tools, and check the console for errors.
If you are posting a message as in examples above or using the embed library to run script:
- If everything went well, in the console you should see Running window message received from origin '[domain]' which was in the accepted list. If this was not expected, this might be an XSS attack. If you see the following, there was probably a problem with the CORS application configuration setting you entered: Attempt to post message from origin '[domain]', but this is not in the allowed list from configuration. Post ignored.
The Product Notes contain some general considerations for embedding.